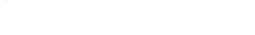[Service] # Remove the cadvisor-port=0 setting to expose the cadvisor metrics Environment="KUBELET_CADVISOR_ARGS=" # allow webhook token authentication. Environment="KUBELET_AUTH_TOKEN_WEBHOOK=--authentication-token-webhook=true --authorization-mode=Webhook" ExecStart= ExecStart=/usr/bin/kubelet $KUBELET_KUBECONFIG_ARGS $KUBELET_SYSTEM_PODS_ARGS $KUBELET_NETWORK_ARGS $KUBELET_DNS_ARGS $KUBELET_AUTH_TOKEN_WEBHOOK $KUBELET_AUTHZ_ARGS $KUBELET_CGROUP_ARGS $KUBELET_CADVISOR_ARGS $KUBELET_CERTIFICATE_ARGS $KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS
Monitoraggio Kubernetes con Prometheus esterno al kube
Il monitoraggio di cluster Kubernetes automatizzato con un Prometheus esterno al kube
Kubernetes
Il [Kubernetes] (o k8s) è una piattaforma self-healing e opensource per l’automazione dei deploy, l’orchestrazione dinamica e la gestione delle applicazioni nei container.
Tutto il progetto Kubernetes ha abbracciato la tecnologia Prometheus e quindi offre supporto al relativo protocollo per il monitoraggio sui servizi presenti nella suite k8s con tanto di alert e generazione automatica di pannelli con grafici (CPU, Rete,…) che diventano fondamentali per evitare interruzioni e analizzare disservizi in genere.
Diverse modalità di monitoraggio
Il montoraggio del cluster può essere effettuato tramite tipologie diverse di architetture:
tramite il [Prometheus Operator] (progetto Opensource della CoreOs) interno al k8s
tramite un Prometheus esterno al cluster k8s che si integra con il Service Discovery del k8s
In questo articolo ci occupermo della seconda ipotesi, il monitoraggio tramite un Prometheus esterno al k8s.
Prerequisiti del k8s per il monitoraggio dall’esterno
Ma come può il mio Prometheus accedere alle metriche dei Pod e dei Container?
Grazie all’integrazione tra Prometheus è k8s è possibile prelevare le metriche del cluster utilizzando l’API del k8s, le API fanno da proxy verso le metriche esposte automaticamente all’interno del cluster dai pod e dal cAdvisor.
Affinchè questa integrazione funzioni è necessario che l’API del Kubernetes sia abilitata all’utenticazione tramite auth token e che il cAdvisor sia abilitato all’interno del cluster. Ma andiamo per gradi.
cAdvisor
cAdvisor is an open source container resource usage and performance analysis agent. It is purpose-built for containers and supports Docker containers natively. In Kubernetes, cAdvisor is integrated into the Kubelet binary. cAdvisor auto-discovers all containers in the machine and collects CPU, memory, filesystem, and network usage statistics. cAdvisor also provides the overall machine usage by analyzing the ‘root’ container on the machine.
Enable auth token & cAdvisor in k8s
Note | […] the kubelet uses token authentication and authorization, as otherwise Prometheus needs a client certificate, which gives it full access to the kubelet, rather than just the metrics. Token authentication and authorization allows more fine grained and easier access control. This means the kubelet configuration must contain these flags:
|
Kubelet is a systemd service running on the Kubernetes master and on each of the Kubernetes nodes. As of version 1.10, kubeadm configures the kubelet service via command line arguments defined in /etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d/10-kubeadm.conf.
As shown in the kube-prometheus-on-kubeadm documentation, we need two changes:
Remove the cadvisor-port=0 flag in order to enable the cadvisor.
Add the —authentication-token-webhook=true flag.
Instead of modifying the file 10-kubeadm.conf, we create a new file 11-kube-prometheus.conf. These files are applied in alphabetical order, so settings in the our file will overwrite the original settings from 10-kubeadm.conf.
Our 11-kube-prometheus.conf file looks like this:
Note that in order to override ExecStart, we first need to make it empty and then re-define it. Otherwise we would just be adding an additional command instead of replacing the command.
Avvio del servizio Prometheus esterno al k8s
Come sempre noi consigliamo di gestire il [Prometheus] esterno tramite [Docker] in modo da semplificarne la configurazione e la sua gestione nel tempo.
version: '3'
services:
prometheus:
image: prom/prometheus:v2.5.0
container_name: prometheus
ports:
- 9090:9090
restart: always
user: '1000'
volumes:
- "$PWD/promdata:/prometheus"
- "$PWD/promconf:/etc/prometheus:ro"
command: "--config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml --storage.tsdb.retention=90d"
logging:
driver: "json-file"
options:
max-size: "200k"
max-file: "10"Configurazione del Prometheus per utilizzare il Service Discovery k8s
global:
scrape_interval: 15s
evaluation_interval: 15s
external_labels:
monitor: 'SkyTv'
rule_files:
- '/etc/prometheus/prometheus.rules'
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'kubernetes-apiservers'
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
api_server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
tls_config:
ca_file: /etc/prometheus/ca.crt
bearer_token_file: /etc/prometheus/kube-api-token
scheme: https
tls_config:
ca_file: /etc/prometheus/ca.crt
bearer_token_file: /etc/prometheus/kube-api-token
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace, __meta_kubernetes_service_name, __meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name]
action: keep
regex: default;kubernetes;https
- job_name: 'kubernetes-nodes'
scheme: https
tls_config:
ca_file: /etc/prometheus/ca.crt
bearer_token_file: /etc/prometheus/kube-api-token
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: node
api_server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
tls_config:
ca_file: /etc/prometheus/ca.crt
bearer_token_file: /etc/prometheus/kube-api-token
relabel_configs:
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+)
- target_label: __address__
replacement: kubernetes.default.svc
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_node_name]
regex: (.+)
target_label: __metrics_path__
replacement: /api/v1/nodes/${1}/proxy/metrics
- job_name: 'kubernetes-cadvisor'
scheme: https
tls_config:
ca_file: /etc/prometheus/ca.crt
bearer_token_file: /etc/prometheus/kube-api-token
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: node
api_server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
tls_config:
ca_file: /etc/prometheus/ca.crt
bearer_token_file: /etc/prometheus/kube-api-token
relabel_configs:
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+)
- target_label: __address__
replacement: kubernetes.default.svc
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_node_name]
regex: (.+)
target_label: __metrics_path__
replacement: /api/v1/nodes/${1}/proxy/metrics/cadvisorInstallare il Grafana
version: '3'
services:
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana:5.3.2
container_name: grafana
ports:
- 3000:3000
restart: always
volumes:
- "$PWD/data:/var/lib/grafana"
user: '1000'
environment:
GF_SMTP_ENABLED: 'false'Esempi di grafici Grafana
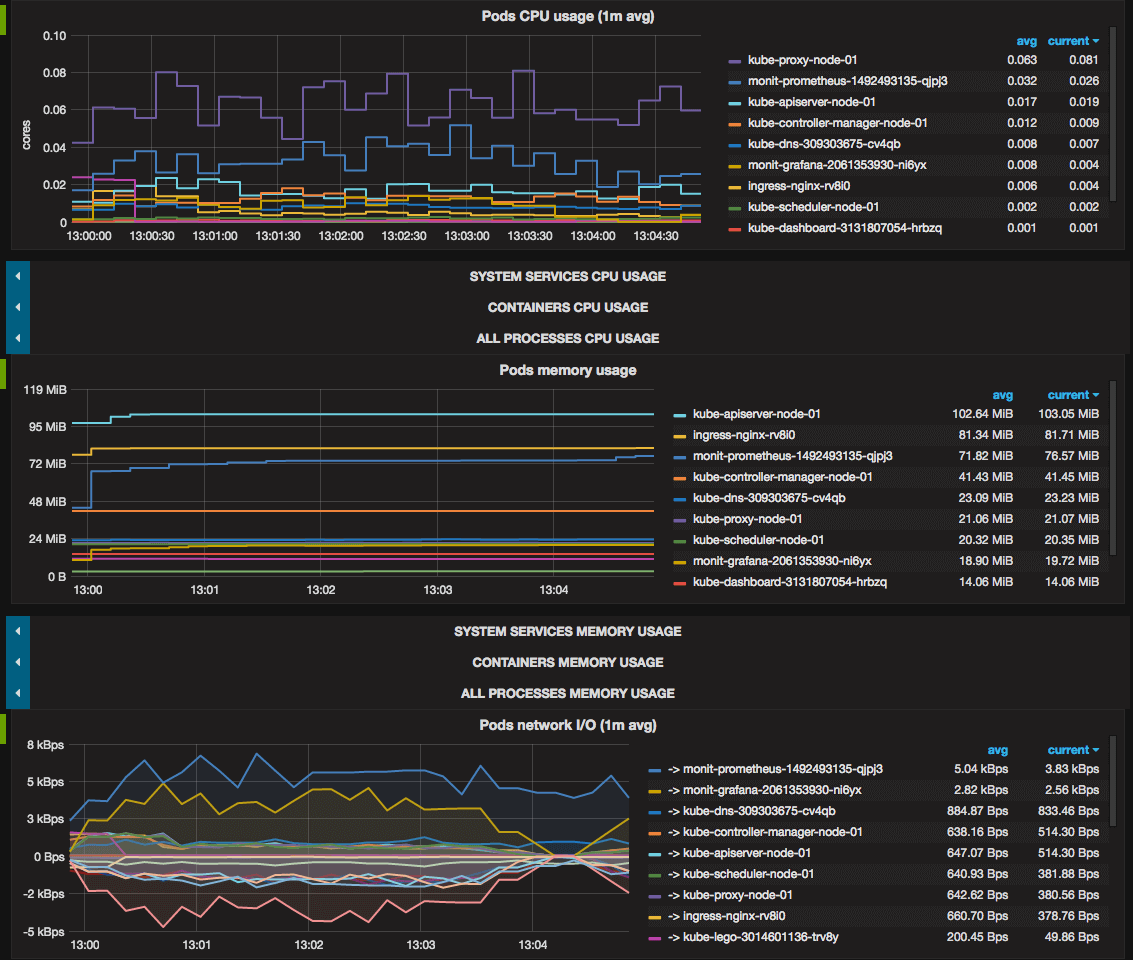
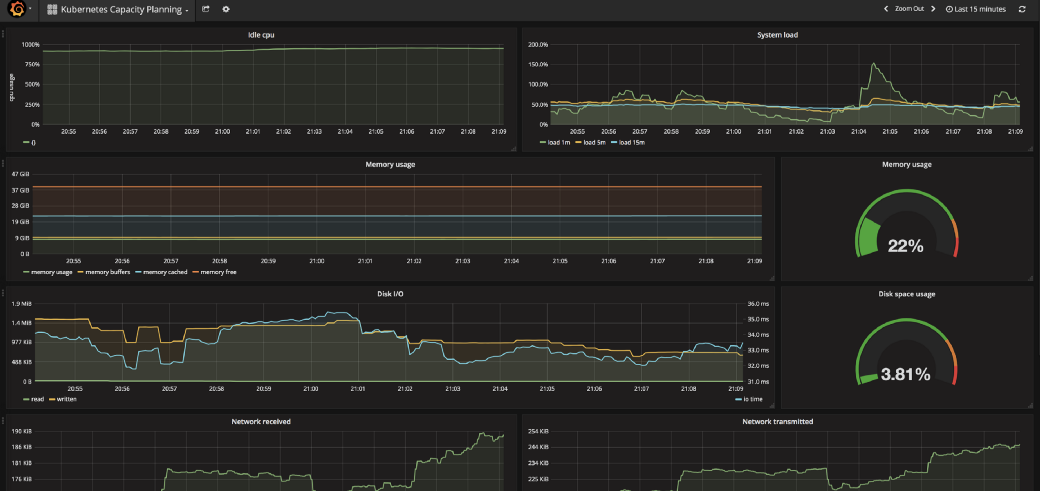
References
[Prometheus] https://prometheus.io/
[Grafana] https://grafana.com
[Prometheus_Operator] https://github.com/coreos/prometheus-operator
[Docker] https://docker.com
[Docker_Compose] https://docs.docker.com/compose/
[Prometheus_2.5.0_binary] https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/releases/download/v2.5.0/prometheus-2.5.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz
[Installing_Grafana_on_RPM-based_Linux] http://docs.grafana.org/installation/rpm/
[Prometheus_Node_Exporter] https://github.com/prometheus/node_exporter
[RedHat_Getting_Started_Orchestrating_Containers_with_kubernetes] https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux_atomic_host/7/html/getting_started_with_kubernetes/get_started_orchestrating_containers_with_kubernetes
Articoli correlati
Monitoraggio Kubernetes con Prometheus
Prometheus Tips: Time based alerts
Prometheus Tutorial: 5 - Recording rules e Federazione
Prometheus Tutorial: 4 - Alert Manager
Prometheus Tutorial: 3 - Exporter
Prometheus Tutorial: 2 - Getting started
Prometheus Tutorial: 1 - Intro
Micrometer, il monitoraggio in Java
Prometheus
Microservizi, Netflix Stack, Spring Cloud